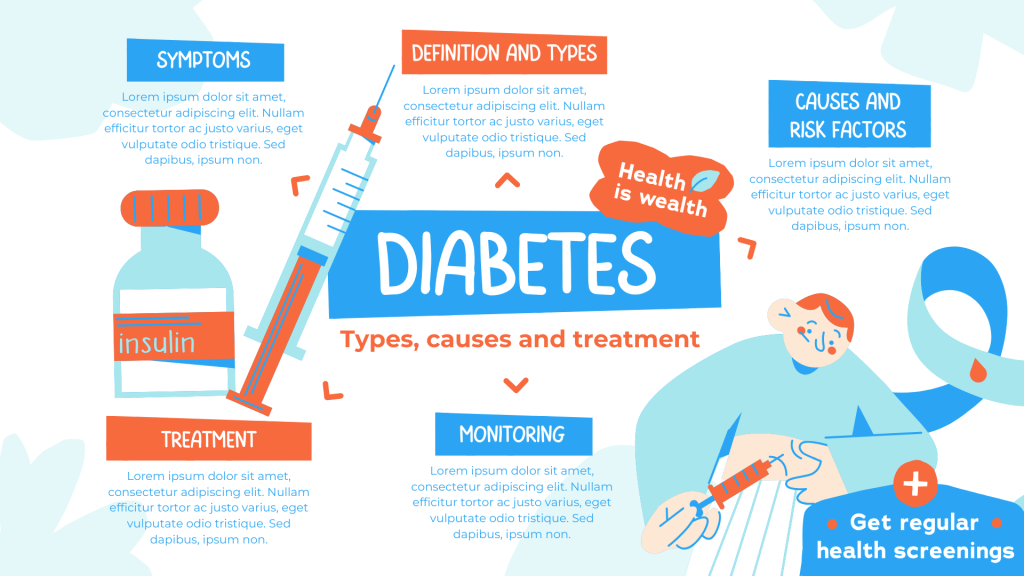
Diabetes, once primarily associated with older adults, is increasingly affecting individuals at a young age, presenting unique challenges and concerns. This chronic condition, characterized by high levels of blood glucose, requires careful management to mitigate its long-term effects on health and quality of life.
There are several factors contributing to the rise of diabetes among young people. Sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and increasing rates of obesity are significant risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes, which accounts for the majority of cases in youth. Additionally, genetic predisposition, family history, and environmental influences play a role in the onset of diabetes at a young age.
The effects of diabetes on young individuals can be profound and far-reaching. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision impairment. Moreover, managing diabetes during critical periods of growth and development can impact academic performance, social interactions, and emotional well-being.
Effective management of diabetes in young individuals requires a multifaceted approach. This includes regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to a balanced diet, engagement in regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medication or insulin therapy. Additionally, education and support from healthcare professionals, family members, and peers are essential for empowering young individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Preventive measures, such as promoting healthy lifestyles and raising awareness about the risk factors for diabetes, are crucial for reducing the incidence of diabetes at a young age. By addressing the underlying causes and providing support for diabetes management, we can improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for young individuals living with diabetes.